最新下载
热门教程
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Drupal7配合Varnish使用及整合drupal模块的详细教程
时间:2022-06-24 22:53:07 编辑:袖梨 来源:一聚教程网
准备环境
首先安装一个全新的Drupal,推荐使用drush安装,方便迅速。
先要建一个数据库,记住用户和密码。
###进入mysql
mysql -uroot -p
CREATE DATABASE `mydb` CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
GRANT ALL ON `mydb`.* TO `username`@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
####退出mysql
Drush安装Drupal7:
drush dl drupal-7.x; #--select 用来选择一个版本
drush site-install standard --account-name=admin --account-pass=admin --db-url=mysql://YourMySQLUser:RandomPassword@localhost/YourMySQLDatabase
默认会安装最新版本的drupal7,如果要选择一个版本,请加参数:–select。
安装成功后,再下载一个varnish模块。
#进入drupal目录
drush dl varnish
安装Varnish
我们默认一个CentOS为例,因为CentOS仓库中的Varnish版本较低,要导入一个新的repo,然后,在升级一下yum软件库。
具体参考这个链接:https://www.varnish-cache.org/installation/redhat
####Varnish 4.0:
rpm --nosignature -i https://repo.va*r*nish-c*ache.org/redhat/varnish-4.0.el6.rpm
yum install varnish
####Varnish 3.0:
###RHEL 5 or a compatible distribution, use:
rpm --nosignature -i https://repo.v*a*rnish-cac*he.org/redhat/varnish-3.0.el5.rpm
yum install varnish
###RHEL 6 and compatible distributions, use:
rpm --nosignature -i https://repo.varnish*-cac*h*e.org/redhat/varnish-3.0.el6.rpm
yum install varnish
#如果安装的版本不对,请update一下。
#yum update
输入如下命令监测是否安装成功:
$ usr/sbin/varnishd -V
varnishd (varnish-3.0.5 revision 1a89b1f)
Copyright (c) 2006 Verdens Gang AS
Copyright (c) 2006-2011 Varnish Software AS
设置Varnish的VCL
复制如下代码到/etc/varnish/default.vcl里面:
| 代码如下 | 复制代码 |
| backend default { .host = "127.0.0.1"; .port = "80"; } sub vcl_recv { if (req.restarts == 0) { if (req.http.x-forwarded-for) { set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = req.http.X-Forwarded-For + ", " + client.ip; } else { set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = client.ip; } } # Do not cache these paths. if (req.url ~ "^/status.php$" || req.url ~ "^/update.php$" || req.url ~ "^/ooyala/ping$" || req.url ~ "^/admin/build/features" || req.url ~ "^/info/.$" || req.url ~ "^/flag/.$" || req.url ~ "^./ajax/.$" || req.url ~ "^./ahah/.$") { return (pass); } # Pipe these paths directly to Apache for streaming. if (req.url ~ "^/admin/content/backup_migrate/export") { return (pipe); } # Allow the backend to serve up stale content if it is responding slowly. set req.grace = 6h; # Use anonymous, cached pages if all backends are down. if (!req.backend.healthy) { unset req.http.Cookie; } # Always cache the following file types for all users. if (req.url ~ "(?i).(png|gif|jpeg|jpg|ico|swf|css|js|html|htm)(?[wd=.-]+)?$") { unset req.http.Cookie; } # Remove all cookies that Drupal doesn't need to know about. ANY remaining # cookie will cause the request to pass-through to Apache. For the most part # we always set the NO_CACHE cookie after any POST request, disabling the # Varnish cache temporarily. The session cookie allows all authenticated users # to pass through as long as they're logged in. if (req.http.Cookie) { set req.http.Cookie = ";" + req.http.Cookie; set req.http.Cookie = regsuball(req.http.Cookie, "; +", ";"); set req.http.Cookie = regsuball(req.http.Cookie, ";(SESS[a-z0-9]+|NO_CACHE)=", "; 1="); set req.http.Cookie = regsuball(req.http.Cookie, ";[^ ][^;]*", ""); set req.http.Cookie = regsuball(req.http.Cookie, "^[; ]+|[; ]+$", ""); # Remove the "has_js" cookie set req.http.Cookie = regsuball(req.http.Cookie, "has_js=[^;]+(; )?", ""); # Remove the "Drupal.toolbar.collapsed" cookie set req.http.Cookie = regsuball(req.http.Cookie, "Drupal.toolbar.collapsed=[^;]+(; )?", ""); # Remove AdminToolbar cookie for drupal6 set req.http.Cookie = regsuball(req.http.Cookie, "DrupalAdminToolbar=[^;]+(; )?", ""); # Remove any Google Analytics based cookies set req.http.Cookie = regsuball(req.http.Cookie, "__utm.=[^;]+(; )?", ""); # Remove the Quant Capital cookies (added by some plugin, all __qca) set req.http.Cookie = regsuball(req.http.Cookie, "__qc.=[^;]+(; )?", ""); if (req.http.Cookie == "") { # If there are no remaining cookies, remove the cookie header. If there # aren't any cookie headers, Varnish's default behavior will be to cache # the page. unset req.http.Cookie; set req.http.X-Varnish-NoCookie = "TRUE"; } else { # If there is any cookies left (a session or NO_CACHE cookie), do not # cache the page. Pass it on to Apache directly. set req.http.X-Varnish-NoCookie = "FALSE"; set req.http.X-Varnish-CookieData = req.http.Cookie; return (pass); } } # Handle compression correctly. Different browsers send different # "Accept-Encoding" headers, even though they mostly all support the same # compression mechanisms. By consolidating these compression headers into # a consistent format, we can reduce the size of the cache and get more hits. # @see: http:// varnish.projects.linpro.no/wiki/FAQ/Compression if (req.http.Accept-Encoding) { if (req.http.Accept-Encoding ~ "gzip") { # If the browser supports it, we'll use gzip. set req.http.Accept-Encoding = "gzip"; } else if (req.http.Accept-Encoding ~ "deflate") { # Next, try deflate if it is supported. set req.http.Accept-Encoding = "deflate"; } else { # Unknown algorithm. Remove it and send unencoded. unset req.http.Accept-Encoding; } } if (req.request != "GET" && req.request != "HEAD" && req.request != "PUT" && req.request != "POST" && req.request != "TRACE" && req.request != "OPTIONS" && req.request != "DELETE") { /* Non-RFC2616 or CONNECT which is weird. */ return (pipe); } if (req.request != "GET" && req.request != "HEAD") { /* We only deal with GET and HEAD by default */ return (pass); } ## Unset Authorization header if it has the correct details... #if (req.http.Authorization == "Basic # unset req.http.Authorization; #} if (req.http.Authorization || req.http.Cookie) { /* Not cacheable by default */ return (pass); } return (lookup); } sub vcl_pipe { # Note that only the first request to the backend will have # X-Forwarded-For set. If you use X-Forwarded-For and want to # have it set for all requests, make sure to have: set bereq.http.connection = "close"; # here. It is not set by default as it might break some broken web # applications, like IIS with NTLM authentication. } # Routine used to determine the cache key if storing/retrieving a cached page. sub vcl_hash { if (req.http.X-Forwarded-Proto == "https") { hash_data(req.http.X-Forwarded-Proto); } } sub vcl_hit { if (req.request == "PURGE") { purge; error 200 "Purged."; } } sub vcl_miss { if (req.request == "PURGE") { purge; error 200 "Purged."; } } # Code determining what to do when serving items from the Apache servers. sub vcl_fetch { set beresp.http.X-Varnish-CookieData = beresp.http.set-cookie; # Don't allow static files to set cookies. if (req.url ~ "(?i).(png|gif|jpeg|jpg|ico|swf|css|js)(?[a-z0-9]+)?$") { # beresp == Back-end response from the web server. unset beresp.http.set-cookie; } else if (beresp.http.Cache-Control) { unset beresp.http.Expires; } if (beresp.status == 301) { set beresp.ttl = 1h; return(deliver); } ## Doesn't seem to work as expected #if (beresp.status == 500) { # set beresp.saintmode = 10s; # return(restart); #} # Allow items to be stale if needed. set beresp.grace = 1h; } # Set a header to track a cache HIT/MISS. sub vcl_deliver { if (obj.hits > 0) { set resp.http.X-Varnish-Cache = "HIT"; } else { set resp.http.X-Varnish-Cache = "MISS"; } } # In the event of an error, show friendlier messages. sub vcl_error { set obj.http.Content-Type = "text/html; charset=utf-8"; set obj.http.Retry-After = "5"; synthetic {" "http://www.**w*3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd"> Error "} + obj.status + " " + obj.response + {""} + obj.response + {" Guru Meditation:XID: "} + req.xid + {" Varnish cache server "}; return (deliver); } |
|
配置完成之后,启动Varnish。
测试效果
打开浏览器,输入druapl7的地址,先看Drupal7是否正常,然后加上端口号。
比如我们的测试地址是:http://drupal7.111com.net
那么再用浏览器打开varnish的地址,如下:http://drupal7.111com.net:6081/
测试结果,两边都正常就表示drupal和varnish都工作正常。
让Varnish缓存Drupal页面
用Firebug查看varnish的请求,如果看到http头里面有X-Varnish的标记表示varnish已经起作用,这时候我们要判断varnish是否缓存了页面。
如何判断:X-Varnish后面有一个数字,表示不是缓存,X-Varnish后面有两个数字,表示缓存成功。
到这里,我们会发现所有的varnish都没有缓存命中,那么问题来了。。。(挖掘机不会出现)
如何让varnish缓存起作用:
// Tell Drupal it's behind a proxy.
$conf['reverse_proxy'] = TRUE;
// Tell Drupal what addresses the proxy server(s) use.
$conf['reverse_proxy_addresses'] = array('127.0.0.1');
// Bypass Drupal bootstrap for anonymous users so that Drupal sets max-age < 0.
$conf['page_cache_invoke_hooks'] = FALSE;
// Make sure that page cache is enabled.
$conf['cache'] = 1;
$conf['cache_lifetime'] = 0;
$conf['page_cache_maximum_age'] = 21600;
给Drupal的settings.php添加如下内容,然后刷新浏览器,即可看到X-Varnish的数字变成了两个(多刷几次)。
至此,Varnish已经完全可以缓存Drupal的页面了。如下图所示:
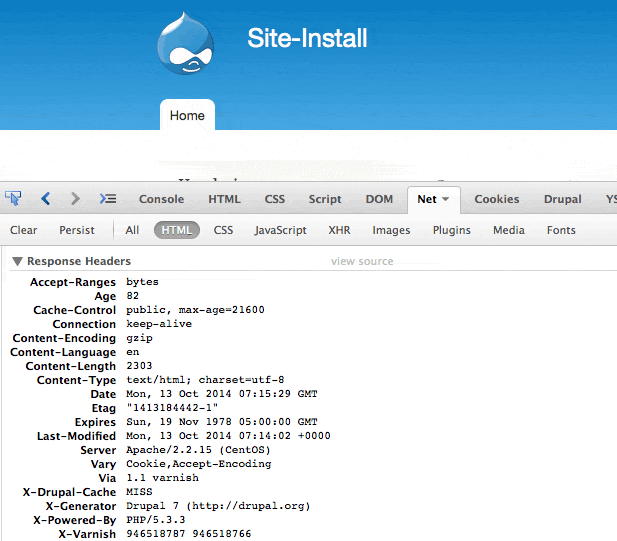
那么,Drupal的Varnish模块是做什么用的?
简单来说,Varnish就是通过Drupal的缓存接口,清除varnish的缓存,比如页面过期。
此外,通过Expire模块,可以精确的控制那些页面,过期时间都可以控制,比较方便。
配置Drupal.org的Varnish模块
启用Varnish模块,阅读一下varnish模块的官方说明: https://www.**dr*upal.org/project/varnish
主要是给Drupal的settings.php添加如下两行:
// Add Varnish as the page cache handler.
$conf['cache_backends'] = array('sites/all/modules/varnish/varnish.cache.inc');
$conf['cache_class_cache_page'] = 'VarnishCache';
然后到Drupal设置页面,路径如下: admin/config/development/varnish
例如:
Varnish Control Terminal: 127.0.0.1:6082
Varnish Control Key: 86b2d660-9768-4a13-ab90-4b0736d6a4d1
点击保存,status就会变为绿色。
(注意:Control Key的值在/etc/varnish/secret 文件里面,复制内容即可)
设置完成,那么清空一下Drupal的缓存,就会发现Varnish里面的缓存值就会刷新,实现了即时清空缓存的目的。
+++++到此完成++++++++(更多问题到drupal大学:http://d*rupal*001*.net提问哦!)+++++
哦哦,还有一种情况,就是Varnish安装再另外一台服务器上,因为Varnish控制后台默认监听的是本机,因此,如果要刷新另一台反向代理服务器的缓存,就必须修改配置。可选的方法有两个,
其一,让Varnish的管理后台地址使用内网的IP(比如192.168.1.x),一般这种架构都是内网集群,因此监听内网也是比较合理的。
其二,本机使用autossh,把本机的端口6082映射到内网机器上面。
$ autossh -fN -L 6082:localhost:6082
完成
至此,Drupal7 + Varnish的配置已经完成,Drupal和varnish也完全集成。Varnish的缓存总得来说速度大于其他缓存,所以可以代替Boost缓存。
如果要使用Varnish缓存动态内容,还有更多的内容要做,本文就不再增加大家的阅读量了(^_^)。
+++++++++++++++++++++++
最后,顺便多嘴,说一下Apache的RPAF Module。
Varnish默认使用 X-Forwarded-For作为远程IP的地址信息,但是这个不是一个标准的协议,有时候我们还是用PHP里面的 $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR']来获得IP。
Apache有一个模块,RPAF的配置文件 rpaf.conf如下,即可获设置正确的IP地址。(具体安装就不多说)
RPAFenable On
RPAFsethostname On
RPAFproxy_ips 127.0.0.1 192.168. 10.0.0.
RPAFheader X-Forwarded-For
相关文章
- jm漫画在线看-jm漫画官网入口 03-11
- 快看漫画app下载入口最新版本-快看漫画app官方正版安装包下载 03-11
- 拷贝漫画APP未删减版下载指南:支持离线缓存的高清漫画阅读神器 03-11
- 差差漫画-登录入口秋蝉视频 03-11
- 羞羞漫画免费登录-羞羞漫画极速入口 03-11
- 漫蛙动漫最新版本下载app-漫蛙动漫官方客户端安装包免费下载入口 03-11














