最新下载
热门教程
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Spring注解@Configuration与@Bean注册组件代码使用解析
时间:2022-06-29 01:44:36 编辑:袖梨 来源:一聚教程网
本篇文章小编给大家分享一下Spring注解@Configuration与@Bean注册组件代码使用解析,文章代码介绍的很详细,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家供大家参考,有需要的小伙伴们可以来看看。
原始Spring开发
Person.java
准备Person.java类:
package com.jektong.spring;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
pom.xml
在pom文件导入Spring基本依赖:
4.0.0 com.jektong maven01 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT maven01 maven01 org.springframework spring-context 4.3.12.RELEASE
bean.xml
在没有使用Spring注解开发之前,我们通常会通过一个xml配置文件(bean.xml)去将我们需要使用的对象通过Bean的方式去注入到Spring容器中。
下面就是将Person作为对象注入Spring容器中:
PersonTest.java
使用一个PersonTest.java测试类测试:
package com.jektong.spring;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 加载配置文件,此文件放在类路径下。
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 获取bean.xml文件中注入的Person对象,并输出。
Person bean = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
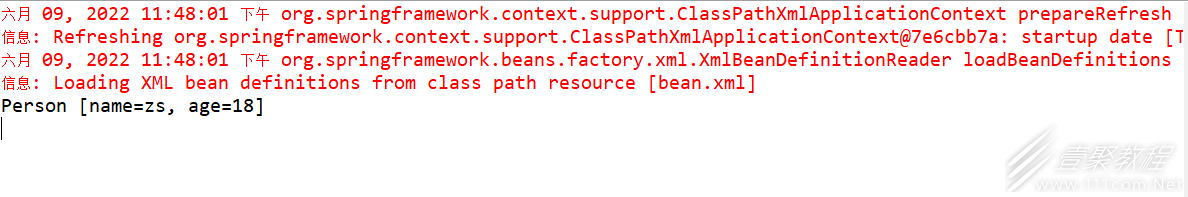
输出结果如下:
注解Spring开发
舍弃上面的bean.xml文件,通过注解的方式将xml文件转换成配置类,建立PersonConfig配置类:
package com.jektong.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.jektong.spring.Person;
@Configuration // 告诉spring这是配置类相当于配置文件bean.xml
public class PersonConfig {
// 这是注入到spring容器的对象ID
// 括号内指定唯一ID,不指定则是默认以方法名为唯一ID,相当于:标签中的ID值。
@Bean("person01")
public Person person() {
return new Person("李四",21);
}
}
测试使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类读取注解:
package com.jektong.spring;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.jektong.config.PersonConfig;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PersonConfig.class);
Person bean = ac.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(bean);
// 查看BEAN的id
String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
for (int i = 0; i
输出如下:
@Configuration与@Bean作用总结
@Configuration
相当于spring中的XML配置文件,将此XML文件替代成配置类,声明在类上。
@Bean
相当于XML文件中所配置的各个Bean对象,现声明在方法上,默认以方法名作为注入的Bean的id。
相关文章
- jm漫画-在线观看最新入口 02-28
- Deepseek网页版免费入口-deepseek在线极速体验 02-28
- 哔咔-picacg核心区别 02-28
- 歪歪漫画-免费看歪歪漫画 02-28
- z-libirary软件-强大功能与独特特点 02-28
- 漫蛙manwa2最新版本下载官方正版入口-下载安装教程及常见问题解答 02-28